Since the 20th century, aluminum alloys have emerged as a groundbreaking material, widely adopted in industrial production and integrated into various aspects of society. The subsequent development of aluminum die-casting technology has further enhanced the lightweight, high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and complex-structure-forming capabilities of aluminum die-cast parts—properties that perfectly align with the demands of automotive manufacturing.
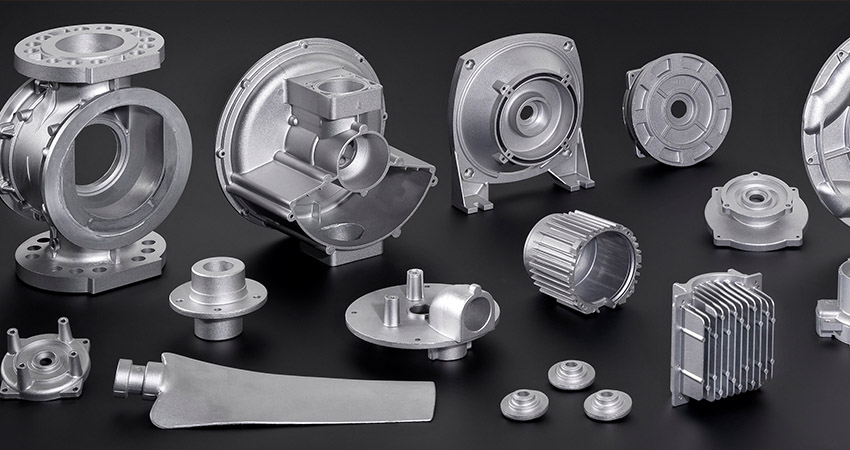

Applications of Aluminum Die-Casting in Automotive Production
1. Powertrain Components
Engine Parts:
Aluminum die-casting is used to manufacture engine blocks, cylinder heads, oil pans, and more. Replacing cast iron with aluminum alloys reduces weight by 30%–50% while maintaining excellent heat dissipation and rigidity (e.g., Volkswagen’s EA888 engine uses die-cast aluminum blocks).
Transmission Housings:
Aluminum die-cast components (e.g., ZF’s 8HP transmission housing) withstand high torque while reducing drivetrain weight, improving fuel efficiency.
2. Body Structural Components
Frame & Crash Protection Parts:
High-strength aluminum alloys (e.g., Al-Si-Mg series) are used to die-cast A/B pillars, sills, and longitudinal beams, enhancing crash energy absorption (e.g., Tesla Model Y’s mega-cast rear underbody reduces hundreds of weld points).
Doors/Trunk Lids:
Die-cast aluminum hinge brackets and latch mechanisms achieve an optimal balance between lightweighting and durability.
3. Chassis Systems
Suspension Components:
Control arms and steering knuckles made via die-casting (e.g., Mercedes-Benz multi-link suspension parts) reduce unsprung mass, improving handling.
Braking Systems:
Die-cast calipers and brackets (e.g., Brembo aluminum calipers) offer lightweighting and high-temperature resistance.
4. Electric & New Energy Vehicle Parts
Battery Systems:
Large die-cast aluminum battery housings (e.g., CATL’s CTP technology) integrate cooling channels, reducing weight and extending range.
Motor Housing:
Die-cast aluminum motor casings (e.g., BYD’s e-Platform 3.0) balance lightweighting with electromagnetic shielding.
5. Other Functional Parts
Thermal Management:
Die-cast compressor housings and radiator end caps leverage aluminum’s sealing and corrosion resistance.
Interior & Electronics:
Thin-wall die-casting enables lightweight dashboard frames and center console structures with complex designs.
Why Choose Aluminum Die-Cast Parts?
Lightweight Material: Aluminum’s density (2.7 g/cm³) is significantly lower than steel (7.8 g/cm³), aiding emission reduction for ICE vehicles and range extension for EVs while improving handling.
High Strength: Despite being lightweight, die-cast aluminum matches steel in strength, with 25–30% higher tensile strength than sand-cast parts, meeting automotive durability needs.
Design Flexibility: Die-casting allows intricate, high-precision designs—from tiny electronics to large transmission housings—ensuring performance, assembly ease, and structural integrity.
High Production Efficiency: Advanced die-casting techniques and computer-aided optimization enhance output, stability, and safety, outperforming other alloys in mass production.
Cost-Effective: Aluminum’s easier extraction and processing lower costs compared to other metals, aligning with automakers’ cost-reduction goals.
Aesthetic Appeal: The sleek, high-gloss finish of die-cast aluminum enhances visual appeal, complementing modern automotive design.
As aluminum die-casting technology advances, it drives the automotive industry toward lightweighting, high performance, and sustainability, becoming a key process—especially in new energy vehicles.